Hookless Wheels, Rims, and Tires: How They Work and Their Benefits
Modern bicycle wheels can be confusing. There’s a wide assortment of alloys and carbons, varying depths and widths, with continuous technological advancements and countless compatibility standards.
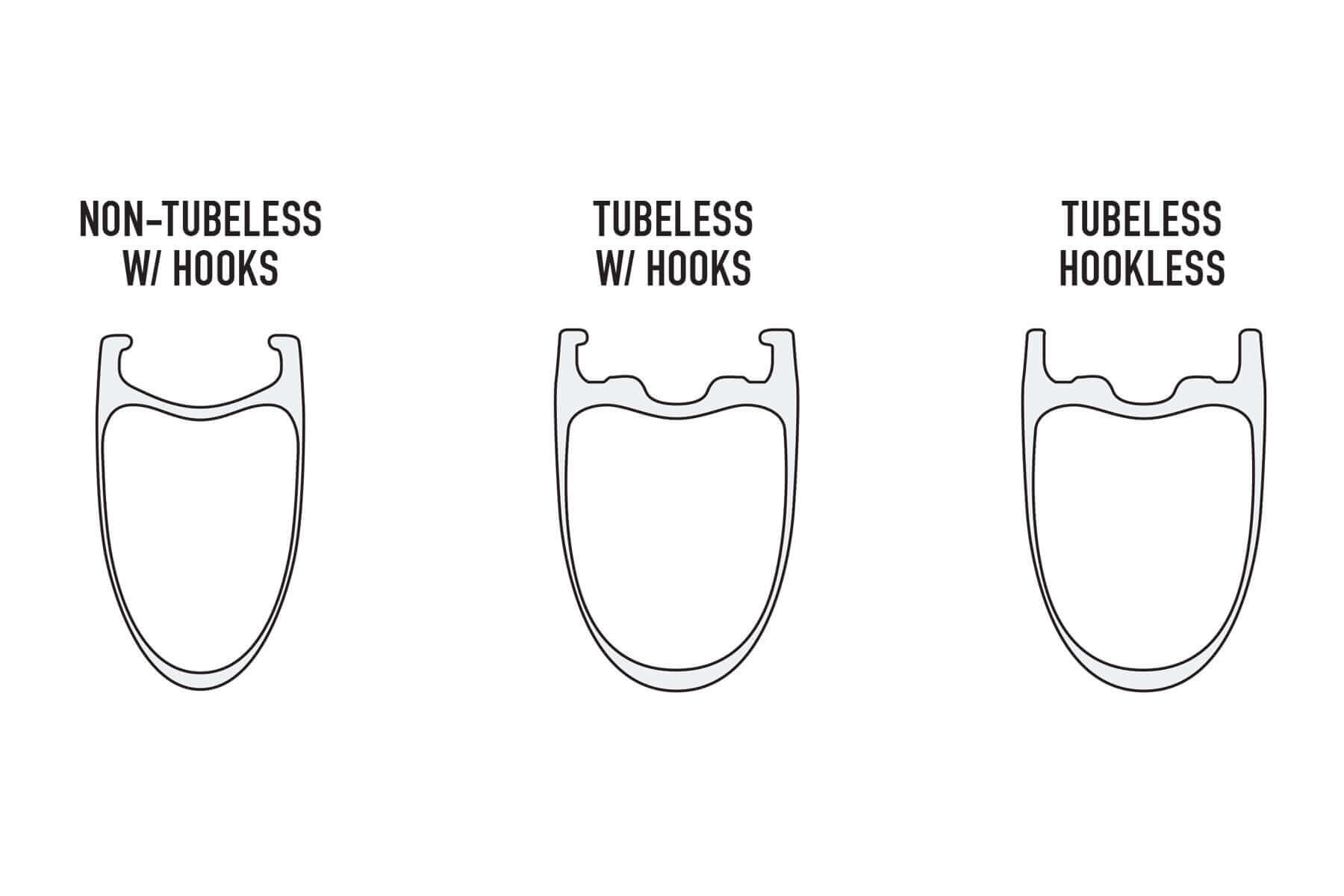
However, how wheels connect to tires has remained relatively consistent for a pretty long time. They historically have included a hook at the edge of the rim that acts as a grip for the tire’s bead when it snaps into place under pressure.
This has remained true even for those with newer tubeless technology.

But one of the newer innovations in cycling wheels is upending that paradigm with a new field of products that ditch the hook in favor of a straight wall or hookless design.
While hookless technology has long been the norm in cars and motorcycles, it has never really taken off similarly in cycling. That is mainly due to wheels and tires, which use an inner tube.
Tubeless wheels have long been the norm in the mountain bike world, but many road and gravel riders still lean toward tubes, favoring higher pressures.
But top-tier wheel makers, including ENVE, Zipp, Cadex, and Corima, have all jumped onto the hookless wagon, among many others. So we may be witnessing a significant change in market norms.
How Do Hookless Rims Work?
In tires with tubes, the rim bead helps mold the inner tube to the tire and wheel at the interior interface. Without an inner tube, it becomes unnecessary. However, connecting the two without a hooked bead requires more precision.

According to Zipp, when seating tires to a hookless wheel, air pressure expands in all directions, pushing the tire’s bead firmly onto the sidewall and locking it into place, provided they are appropriately matched.
Unlike tubed or tubeless tires that are comparable with any wheel of the corresponding size, hookless wheels and tires must match precisely to ensure a consistent and reliable seal.
How precise? In a video produced by Zipp in 2021, the brand said it adopted standards from the European Tire and Rim Technical Organization (ETRTO) with only ±0.1 mm, or about the equivalent of the width of a human hair.
Provided the wheels and tires interface properly, they should hold just as consistently as any other setup.
Challenges to Hookless Rims
One current problem in the hookless universe is that many tires are still manufactured to the specifications of tubeless, hooked-rim setups, so their compounds and design may not be sturdy enough to hold up on a hookless rim.
While some companies like Zipp have adopted ETRTO standards that make pairing easier, there is currently no universal standard for hookless wheels and tires to bring everything together.
“Rim manufacturers have outpaced the rate at which some tire manufacturers have innovated, creating a complicated environment for consumers when it comes to pairing tires with their new state-of-the-art hookless road or gravel rims,” ENVE said in a 2019 guide to hookless technology and how it works.
That is beginning to change as hookless wheels continue to grow in popularity. But even now, most companies have specific lists of tires that are compatible with their hookless rims. Some are also working directly with tire manufacturers to dial compatibility.
According to Cadex, which falls under the Giant umbrella, tolerances of tire bead diameter and rim bead seat diameter must match up to ensure that tires stay fixed to a rim and allow a rider to stop safely.
“If rim manufacturers do not work directly with tire manufacturers when designing new hookless rims, tolerances and bead materials can vary,” Cadex said. “This can make it difficult to pair tires and hookless rims from different manufacturers.”
Hookless Rim and Tire Benefits
Zipp said the broader rims and lower pressures associated with hookless wheels bring a wealth of benefits to riders.
First, increased rim width allows drops in tire air pressure due to the reduced probability of pinch flats. This lower pressure reduces energy loss through vibration, making traversing bumpy surfaces more efficient and comfortable.
They also improve grip for cornering and wet conditions while creating less tire deformation where the wheels contact the ground. That reduces rolling resistance and decreases energy used to build speed.
Hookless wheels also create a more aerodynamic interface where the tire meets the wheel. Current tubed or tubeless, hooked rim setups clinch to the edge of tires to create a bulge in the tire that juts out beyond the end of the rim.
That extra space, while incredibly minuscule, creates more drag than hookless wheels’ streamlined interface. With hookless wheels, tires are not squeezed at the bead so drastically, so they can retain a more streamlined shape.
ENVE said hookless wheel design results in a more robust final product too. First, cutting out the curve of the traditional hook allows carbon sheets to hold a more natural pattern while allowing for more material along the edge of the wheel to make it stronger. This, ENVE said, leads to more toughness and resistance to hits and a rim that is less expensive to produce.
Hookless Wheel Takeaways
Hookless wheels are nothing new. They have been the standard in transportation for a long time. However, they’ve only recently started to take off in cycling, and more so in the mountain bike world. As standards become clear and companies embrace compatibility, hookless wheels may become the new normal.
As for now, hookless wheels usually present a lighter, less expensive, and more durable option, even if riders may have to be more discerning when choosing which tire to run.
The post Hookless Wheels, Rims, and Tires: How They Work and Their Benefits appeared first on GearJunkie.


